China’s disease control authority has recently introduced a pilot monitoring system to track pneumonia cases of unknown origin. This initiative aims to address the anticipated rise in respiratory infections during winter. Reports indicate a surge in infections across northern provinces, with human metapneumovirus (HMPV) standing out as a significant concern, particularly among younger populations. Despite viral social media speculations about a health emergency, no official announcements have confirmed such claims.
What is Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)?
Human metapneumovirus, identified in 2001, is a respiratory virus belonging to the Pneumoviridae family, which also includes respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). HMPV causes cold-like symptoms and affects both the upper and lower respiratory tracts. It is most active during winter and early spring, posing a higher risk to children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems.
Symptoms of HMPV Infection
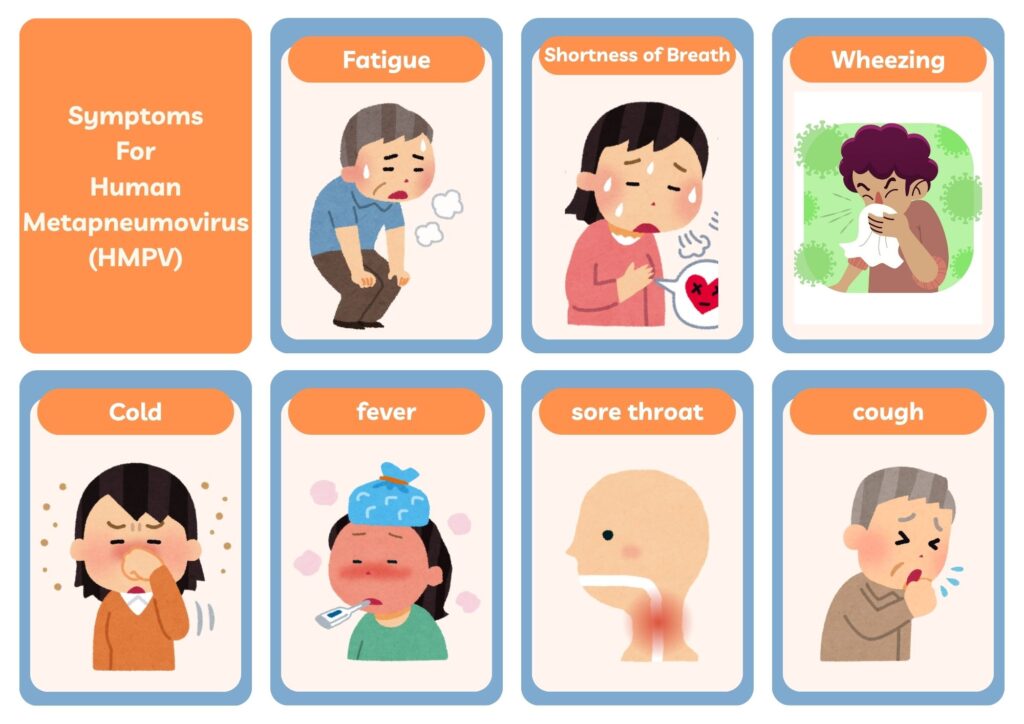
The symptoms of HMPV include:
- Cough
- Runny or blocked nose
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Wheezing
The incubation period typically lasts 3–6 days. While most individuals recover without medical intervention, complications such as bronchitis or pneumonia may arise in severe cases, requiring professional medical care.
How Does HMPV Spread?
HMPV is transmitted through:
- Direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated surfaces.
- Respiratory droplets from coughs or sneezes.
- Close interactions, such as shaking hands or hugging.
- Touching contaminated objects, like phones or doorknobs, and then touching the face.
Treatment for HMPV
Currently, there is no vaccine or specific antiviral treatment for HMPV. Symptom management includes:
- Over-the-counter medications for fever and pain.
- Decongestants for nasal symptoms.
Antibiotics are ineffective, as HMPV is a viral infection.
Preventing HMPV Infection
Preventative steps to minimize HMPV transmission:
- Wash hands frequently with soap and water.
- Avoid close contact with infected individuals.
- Refrain from touching the face, nose, or eyes.
- Wear a mask in high-risk environments.
- Individuals with pre-existing lung conditions should take extra precautions.
Monitoring and Response by Health Authorities
In response to rising cases in China, India’s National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) is closely monitoring respiratory infections. Collaborating with global health agencies, the NCDC is analyzing data to track trends. While acute respiratory infections, including HMPV, are on the rise, the overall severity of respiratory diseases in China is reportedly lower than last year. A seasonal uptick in respiratory pathogens is expected across the northern hemisphere during winter.