White patches on skin are a condition that can cause worry, confusion, or embarrassment for many people. These patches are lighter than the surrounding skin and may appear suddenly or grow slowly over time. While some white patches on skin are harmless and temporary, others may point to underlying health issues that need medical attention.
Understanding White Patches on Skin
White patches on skin are areas where the normal skin color fades because of reduced melanin production. Melanin is the pigment that gives color to our skin, hair, and eyes. When melanin is absent or reduced in a particular area, it creates white patches on skin. These patches can be small, round spots or larger irregular patches depending on the cause.
Major Causes of White Patches on Skin
There are many possible reasons behind white patches on skin. Some are harmless, while others may require regular treatment.
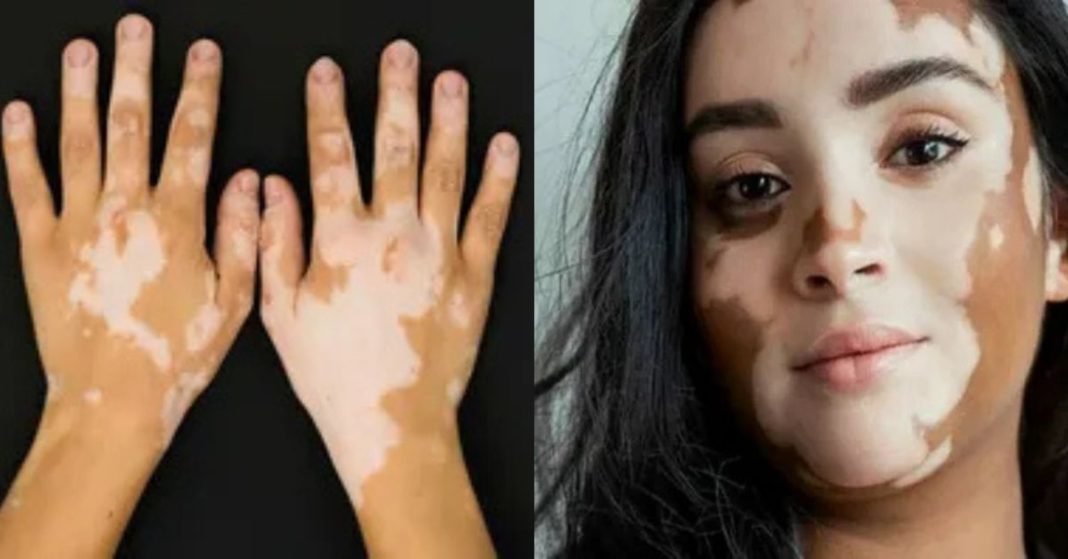
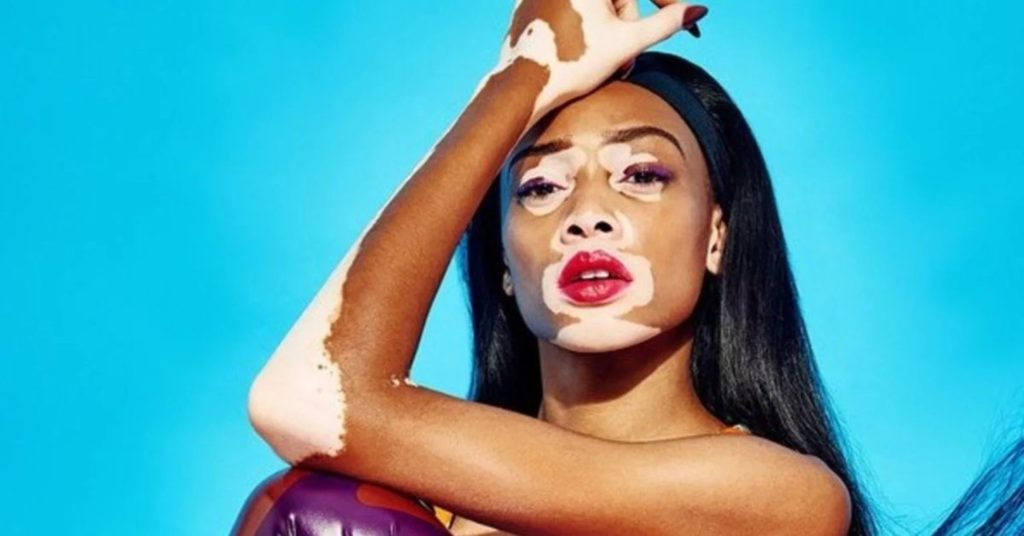
Vitiligo: An Autoimmune Cause of White Patches on Skin
- Vitiligo is a condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the cells that produce melanin.
- White patches on skin from vitiligo often start around the mouth, eyes, hands, or feet and may gradually spread.
- This condition is not painful or contagious, but it can affect a person’s confidence.
Fungal Infections (Tinea Versicolor) and White Patches on Skin
- Tinea versicolor is a common fungal infection that causes small, round, white patches on skin, usually on the chest, shoulders, and back.
- These patches may become more visible in the summer due to sweating and sun exposure.
- Mild itching or scaling may accompany the patches.
Pityriasis Alba: Common in Children
- This condition usually affects children and teenagers.
- White patches on skin caused by pityriasis alba often appear on the face, neck, and arms.
- They may look dry or scaly but generally fade with age and proper skin care.
Nutritional Deficiencies Leading to White Patches on Skin
- Lack of essential vitamins and minerals, such as Vitamin B12, Vitamin D, and copper, can lead to white patches on skin.
- Poor diet or long-term illnesses may increase the risk.
- Including green leafy vegetables, nuts, eggs, and dairy in the diet can help.

Skin Conditions Like Eczema and Psoriasis
- Both eczema and psoriasis may leave behind light-colored patches once the inflammation heals.
- These white patches on skin may not last forever but can be bothersome.
Sun Damage and White Spots
- Too much sun exposure can sometimes damage skin cells, leading to small white spots, especially on the arms and legs of fair-skinned people.
- Using sunscreen regularly helps prevent this.
Common Symptoms of white spots on the skin
Not all white patches on skin are the same. Some important symptoms to watch out for include:
- Light-colored patches that grow over time
- Dry, scaly, or itchy patches
- Hair in the affected area turning white
- Redness or inflammation around the patches
- Uneven skin tone on sun-exposed areas
Diagnosis of white spots on the skin
A doctor may use different methods to find the exact cause of white patches on skin:
- Physical Examination: Checking the size, shape, and spread of the patches
- Wood’s Lamp Test: Using special ultraviolet light to study the patches
- Blood Tests: To check for vitamin deficiencies or immune problems
- Skin Biopsy: Taking a small sample of skin to examine under a microscope
Treatment Options for white spots on the skin
The treatment for white patches on skin depends on the underlying cause.
Medicinal Creams and Lotions
- Steroid creams may help reduce inflammation and bring back skin color in conditions like vitiligo or eczema.
- Antifungal creams or shampoos are used if a fungal infection is the cause.
Light Therapy for white spots on the skin
- Phototherapy (light therapy) uses special rays of light to stimulate pigment cells and improve the color of the skin.
- It is commonly used for spreading vitiligo.
Nutritional Supplements and Diet
- Vitamin B12, Vitamin D, and minerals like zinc and copper are often recommended for people with nutritional deficiencies causing white patches on skin.
- A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and nuts is essential.
Skin Care and Home Remedies
- Moisturize daily to prevent dryness.
- Always use sunscreen to protect sensitive patches.
- Avoid harsh soaps, chemicals, or skin irritants.
- Coconut oil and aloe vera gel can soothe mild patches naturally.
Advanced Treatments
- In severe vitiligo, surgical options like skin grafting or melanocyte transplant may be considered.
- These are usually chosen only when other treatments do not show results.
Preventing white spots on the skin
Although not all white patches can be prevented, you can reduce the chances by following these tips:
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Use sunscreen regularly to avoid sun damage.
- Treat fungal infections and skin rashes at an early stage.
- Maintain good personal hygiene.
- Avoid stress, as it may trigger or worsen autoimmune conditions like vitiligo.
Myths and Facts About white spots on the skin
- Myth: White patches on skin spread by touch.
- Fact: Most causes, such as vitiligo or pityriasis alba, are not contagious.
- Myth: Only adults develop white patches.
- Fact: Children and teenagers can also be affected.
- Myth: White patches on skin are always permanent.
- Fact: Some causes like fungal infections or pityriasis alba improve with treatment and care.
When to See a Doctor About white spots on Skin
Seek medical advice if you notice:
- Rapidly spreading white patches
- Patches that cause itching, pain, or burning
- Hair in the patches turning white
- Large or very visible patches that affect confidence
Conclusion
White patches on skin can happen to anyone, from children to adults, and they are usually not dangerous. The key is to understand the cause — whether it’s vitiligo, a fungal infection, or a vitamin deficiency — and treat it on time. With the right medical help, healthy diet, and good skin care, most people can manage or reduce the appearance of white patches on skin effectively. Early attention and proper care ensure that the skin remains healthy and confident.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About white spots on the skin
1. What are white spots on the skin?
White patches on skin are areas where the skin loses its natural color due to reduced melanin production. They may appear as small spots or large patches and can have many different causes such as vitiligo, fungal infections, or vitamin deficiencies.
2. Are white patches on skin dangerous?
Most white patches on skin are not dangerous. However, they may sometimes indicate conditions like vitiligo, eczema, or nutritional deficiencies. If the patches spread quickly or cause itching, pain, or hair loss, it is important to see a doctor.
3. Can skin whitening patches spread from one person to another?
No, most causes of white patches on skin — including vitiligo and pityriasis alba — are not contagious. A fungal infection like tinea versicolor can spread only through direct skin contact or by sharing clothes, towels, or personal items.
4. How are skin whitening patches diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose white patches on skin through physical examination, Wood’s lamp test, blood tests to check for vitamin deficiencies, or a skin biopsy if needed. The method depends on the suspected cause of the patches.
5. What are the main treatments for white spots on the skin?
Treatments for white patches on skin include antifungal creams, steroid-based creams, light therapy (phototherapy), vitamin and mineral supplements, and in rare cases, surgical options like skin grafting. Simple skin care routines like moisturizing and sun protection also help.
6. Can diet help reduce white spots on the skin?
Yes, eating a balanced diet rich in Vitamin B12, Vitamin D, copper, zinc, and iron can help in preventing or reducing white patches on skin caused by nutritional deficiencies. Including leafy greens, nuts, eggs, dairy products, and fresh fruits is beneficial.
7. Do white spots on the skin go away on their own?
It depends on the cause. White patches on skin due to pityriasis alba or fungal infections often fade with treatment and time. However, vitiligo usually requires long-term care and may not fully go away without treatment.
8. When should I consult a doctor about white spots on the skin?
You should consult a doctor if the white patches on skin spread rapidly, cause itching or pain, appear on visible areas like the face, or if the hair within the patches turns white. Early medical care helps in better treatment results.