IMEC Faces Challenges as the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC), launched in 2023, grapples with significant hurdles that threaten its ambitious goal of enhancing trade and connectivity between India, the Arabian Gulf, and Europe. Designed to reduce shipping times by 40% compared to traditional routes, IMEC aims to revolutionize global trade through a multi-modal infrastructure network. However, recent geopolitical conflicts in the Middle East, particularly the Israel-Gaza conflict and deteriorating regional relations, have severely impeded progress. This article explores IMEC’s purpose, its strategic importance, the challenges it faces, and its current status amidst an unstable geopolitical landscape.
What is the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor?
IMEC, or the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor, is a transformative multi-modal trade and connectivity project that links India’s western ports to Europe via the Arabian Gulf. IMEC Faces Challenges in executing its two primary legs: the India-Gulf corridor and the Gulf-Europe corridor. Goods are transported from Indian ports to the UAE, then moved via high-speed rail through Saudi Arabia and Jordan to Israel’s port of Haifa. From Haifa, cargo ships travel to Greece and Italy, where European rail networks distribute goods across the continent. Beyond trade, IMEC aims to enhance digital connectivity, promote clean energy exports, and create jobs, positioning itself as a counter to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
Strategic Importance of IMEC
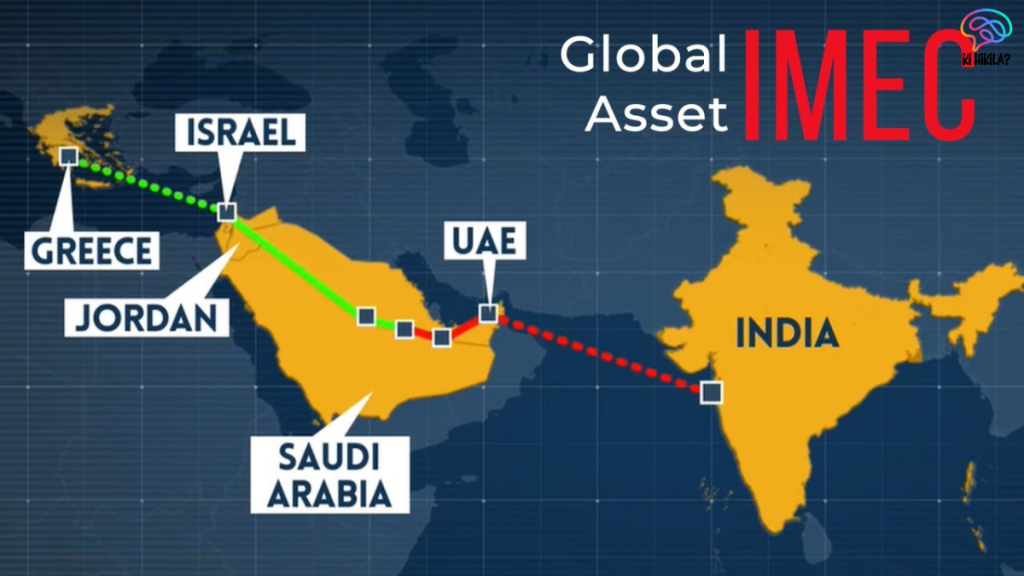
Announced during India’s G20 presidency in 2023, IMEC capitalized on a rare period of Middle Eastern stability, leveraging improving relations between Arab states and Israel, as well as strengthening trade ties between India, the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and the European Union. The EU, India’s largest trading partner, saw bilateral trade surpass $137 billion in 2023-24. IMEC Faces Challenges in realizing its potential to streamline trade, reduce transit costs, and lower emissions by integrating advanced infrastructure and digital networks. The corridor also aligns with global goals of sustainable development, fostering economic interdependence to promote regional stability and counterbalance China’s growing influence in the Middle East.
Geopolitical and Operational Challenges
IMEC Faces Challenges primarily due to escalating geopolitical tensions in the Middle East. The ongoing Israel-Gaza conflict has disrupted the corridor’s progress by straining Jordan-Israel relations and halting Saudi Arabia’s normalization talks with Israel, largely due to unresolved Palestinian statehood issues. These tensions have increased insurance costs and security risks for shipping routes, particularly around Haifa, a critical hub for IMEC. The expansion of hostilities in Lebanon, Yemen, Syria, and Iraq, coupled with rising tensions with Iran, further complicates the corridor’s viability. IMEC Faces Challenges as these conflicts shift focus from operational logistics to fundamental geopolitical barriers, undermining the regional cooperation essential for the project’s success. Additionally, competition between Saudi Arabia and the UAE for regional dominance adds another layer of complexity, potentially hindering coordinated efforts.
Current Status and Future Prospects
Despite these setbacks, the eastern leg of IMEC, involving India, the UAE, and Saudi Arabia, continues to show promise due to strong bilateral partnerships. India’s robust trade relationships with these Gulf states, bolstered by initiatives like UPI-based digital payments, provide a foundation for progress. For instance, India’s non-oil trade with the UAE has grown significantly, and Saudi Arabia remains a key energy partner. However, IMEC Faces Challenges in the western leg, particularly due to security concerns around Haifa and the stalled normalization of Arab-Israel relations. The corridor’s full realization hinges on restoring regional stability, particularly resolving the Palestinian conflict. Until these geopolitical conditions improve, IMEC remains a strategic vision rather than an operational reality.
Path Forward for IMEC

IMEC Faces Challenges that require strategic patience and diplomatic efforts to overcome. The eastern leg’s progress suggests that focusing on incremental advancements, such as strengthening India-Gulf infrastructure and digital connectivity, could keep the project alive. India’s proactive role, evidenced by recent diplomatic engagements, underscores its commitment to IMEC’s long-term success. However, addressing regional instability, fostering inclusive dialogue with excluded players like Egypt and Turkey, and securing clear financial commitments are critical next steps. IMEC’s potential to transform global trade remains immense, but its success depends on navigating the complex geopolitical landscape of the Middle East.



